There’s a running conversation in the restaurant industry about delivery’s impact on margins, and now investment advisor Hedgeye Risk Management has crunched the numbers in a range of scenarios, including how much delivery impacts the total volume, as well as incrementality and various commission rates.
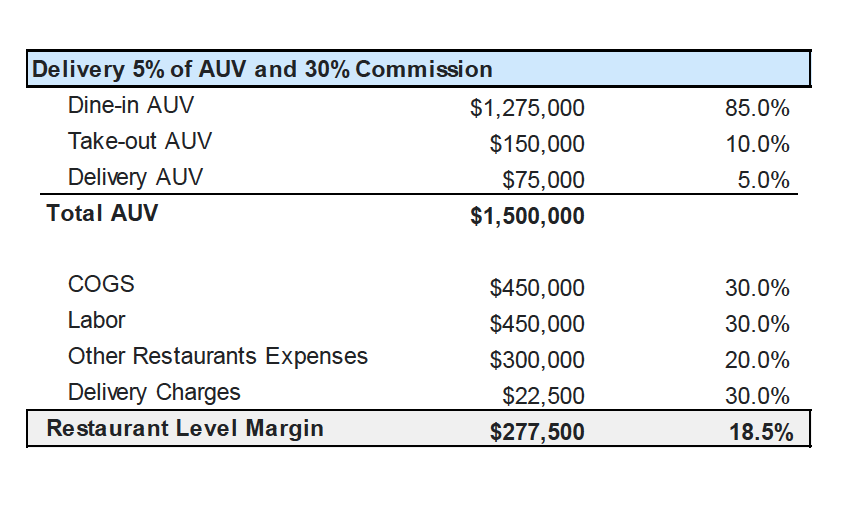
Hedgeye’s first scenario assumes that delivery is 5 percent of a hypothetical restaurant’s average unit volume, $75,000 in sales for total annual sales of $1.5 million. Assuming a 30 percent fee for delivery, that’s a $22,500 hit to the bottom line, for a total restaurant level margin of $277,500. The report adds that delivery is so small for most restaurant operators that it “hasn’t been particularly taxing on the financials.” In this base scenario, the report concludes, “30 percent commissions are not debilitating at just 5 percent of sales.”
The second scenario examines the impact of delivery rising to 10 percent of a restaurant’s AUV with a 30 percent commission paid to delivery providers. With delivery taking a larger share of the total, the restaurant level margin would decrease $22,500 to $255,000.
Going deeper, Hedgeye extrapolates the impact of delivery at 10 percent of total sales, but a lower 15 percent commission. This results in a total margin of $277,500, the same 18.5 percent profit margin as the base scenario. The study notes, “high commission rates deserve some pushback for operators that are already facing inflation in other parts of their business such as labor.”
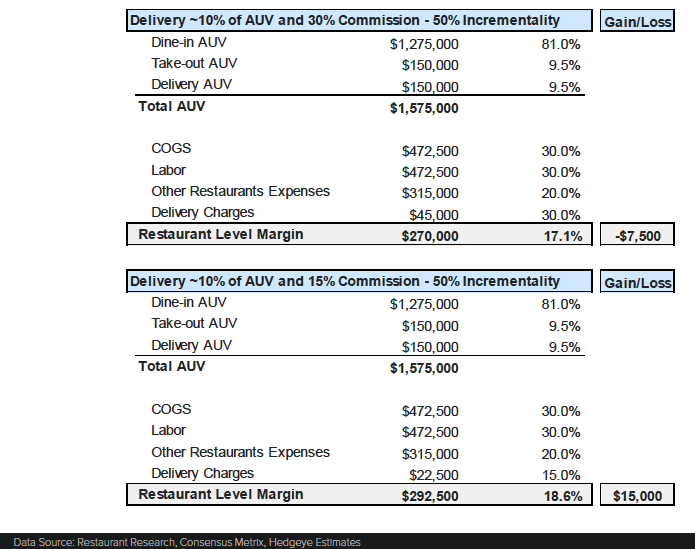
Diving specifically into incrementality, the final two scenarios assume delivery is 10 percent of AUV and 50 percent incremental (meaning half of the delivery sales are new to the restaurant and not cutting into dine-in volume). Running these numbers with 30 percent and 15 percent delivery commissions also produces a $22,500 swing in total restaurant level margin. In this scenario, a 30 percent commission results in a total margin of $270,000 compared with $292,500 on a 15 percent commission. “Even with 50 percent incrementality, 30 percent commission rates on an increasing share of the business are tough to deal with,” the report concluded.
Having nosed around my fair share of delivery reports, Hedgeye’s latest study is particularly notable for diving into these scenarios with specificity. If the prevailing restaurant exec wisdom holds true, that delivery’s incrementality is decreasing as the convenience becomes more ubiquitous, more restaurants will be trying to negotiate lower commissions as the impact on restaurant-level margins becomes more pronounced and, therefore, less sustainable over time.